Base Functions¶
EcoPy contains several basic functions:
-
wt_mean(x, wt=None)¶ Calculates as weighted mean. Returns a float.
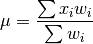
Parameters
- x: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of input observations
- wt: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of weights. If this vector does not sum to 1, this will be transformed internally by dividing each weight by the sum of weights
Example
Weighted mean:
import ecopy as ep print ep.wt_mean([1,3,5], [1,2,1])
-
wt_var(x, wt=None)¶ Calculates as weighted variance. Returns a float.
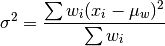
where
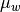 is the weighted mean.
is the weighted mean.Parameters
- x: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of input observations
- wt: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of weights. If this vector does not sum to 1, this will be transformed internally by dividing each weight by the sum of weights
Example
Weighted variance:
import ecopy as ep print ep.wt_var([1,3,5], [1,2,1])
-
wt_var(x, wt=None) Returns a vector of scaled, weighted observations.
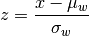
where
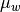 is the weighted mean and
is the weighted mean and 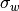 is weighted standard deviation (the square root of weighted variance).
is weighted standard deviation (the square root of weighted variance).Parameters
- x: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of input observations
- wt: numpy.ndarray or list
- A vector of weights. If this vector does not sum to 1, this will be transformed internally by dividing each weight by the sum of weights
Example
Weighted variance:
import ecopy as ep print ep.wt_scale([1,3,5], [1,2,1])